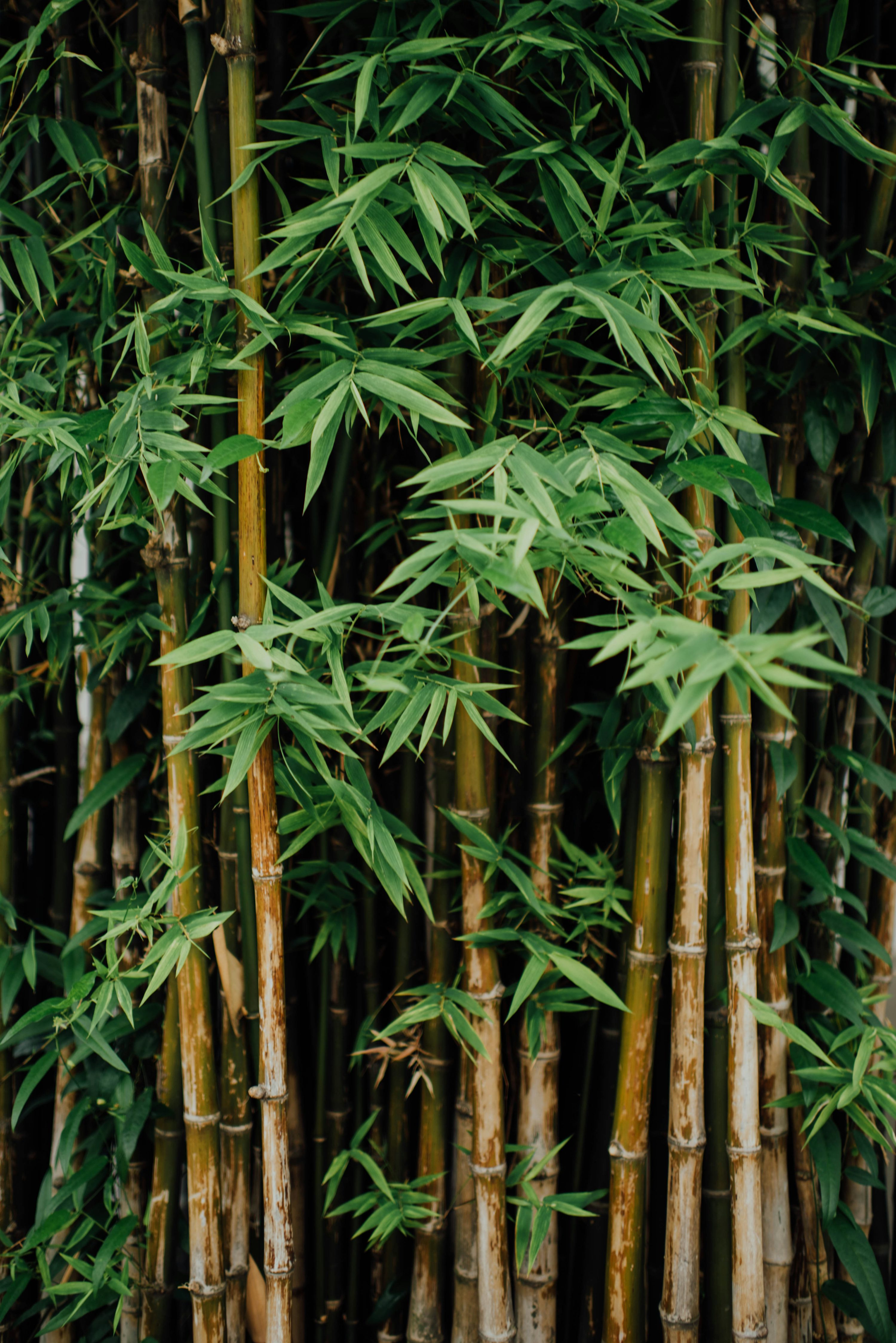
Bamboo
- Family: Poaceae
- Local Names: Hindi, it is referred to as Bans or Bamboo, Bengali, it is called Bans or Bamboo, Telugu, it is known as Bommaka or Bamboo, Kannada, it is called Bande or Bamboo, and in Malayalam, it is referred to as Muthalam or Bamboo. In Marathi and Gujarati, it is commonly known as Bamboo or Bans.
Description
1. Bamboo is a perennial, evergreen plant that belongs to the grass family (Poaceae). It is characterized by its tall, woody, and hollow stems, known as culms, which can grow rapidly, often reaching heights of 30 to 100 feet (9 to 30 meters) within a few months, depending on the species. The stems are segmented by nodes, from which leaves and branches emerge.
2. Bamboo leaves are long, narrow, and typically lanceolate in shape, with a bright green color that deepens as they mature. The plant is highly adaptable, thriving in various climates ranging from tropical to temperate regions. It is also known for its resilience, being able to regenerate quickly after being harvested.
Ecology
Bamboo plays a significant role in various ecosystems, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. It thrives in diverse soil types but prefers well-drained soils with ample sunlight. Bamboo groves can stabilize soil, prevent erosion, and create habitats for various wildlife. Its rapid growth and ability to regenerate quickly make it an important species for ecological restoration and sustainability.
Tree Management
Bamboo is managed through a process called clump management or thinning. It can be propagated via seeds, but more commonly through vegetative methods like rhizome or culm cuttings. Proper management involves selecting suitable species for the intended use, maintaining adequate spacing to avoid overcrowding, and periodic thinning to ensure healthy growth. Bamboo requires regular irrigation and occasional fertilization to optimize growth and productivity.
Timber
Bamboo timber is highly valued for its strength, flexibility, and lightweight properties. It is used in construction, furniture, and flooring, and is known for its sustainability as a renewable resource. The timber's versatility allows it to be processed into various forms, including poles, panels, and laminates. Bamboo’s natural durability and resistance to pests make it an ideal material for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Shade or Shelter
Bamboo provides excellent shade and can be used effectively for creating natural shelters. Its dense foliage and tall culms offer cooling shade, making it useful for landscaping and garden design. Bamboo groves can also serve as windbreaks and noise barriers, enhancing comfort and privacy in residential and commercial spaces.
Medicine
In traditional medicine, bamboo is used for its various therapeutic properties. Different parts of the bamboo plant, including the shoots, leaves, and stems, are used to treat ailments such as digestive issues, respiratory problems, and skin conditions. Bamboo extract and powders are also used in dietary supplements and herbal remedies, reflecting its role in holistic health practices.
Gum or Resin
Unlike some other plants, bamboo does not produce a significant amount of gum or resin. Instead, its value lies in its structural properties and versatility. However, bamboo can be processed into various products that may include adhesive applications, but it does not naturally secrete resin like some other trees. Its primary uses are in construction, crafts, and as a sustainable resource.